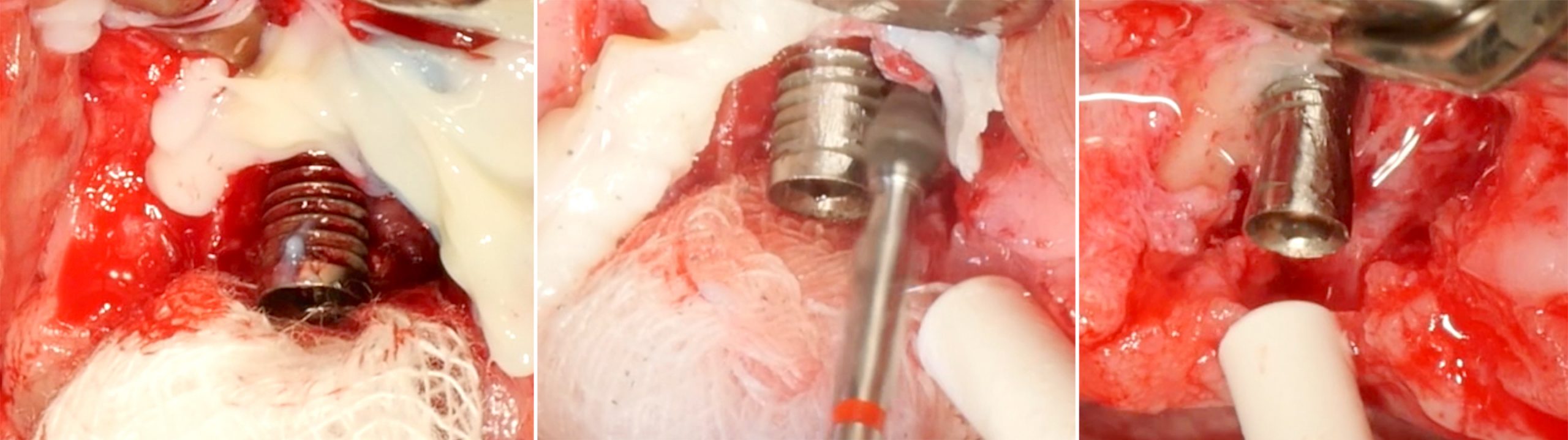
Peri-implantitis often develops quietly around dental implants, and understanding how specialists manage this condition helps patients protect their oral health while feeling more informed and confident during treatment decisions.
What makes peri-implantitis a unique implant complication?
Peri-implantitis stands apart from other implant complications because it creates inflammation and bone loss around an implant that normally integrates firmly with surrounding tissue. According to our editor’s research, clinicians describe this condition as both inflammatory and structural, meaning it requires attention to soft tissue health as well as bone stability. As the inflammation develops, harmful bacteria accumulate in pockets that form around the implant. These pockets gradually deepen and allow bacteria to spread further. People often remain unaware of the early signs because discomfort appears slowly rather than suddenly. Understanding this unique pattern helps patients recognize the importance of early evaluation and timely care.
Why do early symptoms deserve quick attention?
Early symptoms matter because they signal tissue changes that can progress rapidly if left untreated. Peri-implantitis often begins with mild swelling, slight bleeding, or subtle discomfort during brushing. As a result of our editor’s reviews, specialists report that many patients ignore these early changes because they feel mild compared to natural tooth pain. However, even minimal symptoms indicate bacterial activity that may already be affecting bone support. Early detection allows clinicians to slow or stop the damage before long-term stability is threatened. Patients benefit from quicker recovery when issues are addressed promptly. Paying attention to small symptoms prevents larger problems in the future.
How do specialists diagnose peri-implantitis accurately?
Diagnosis relies on careful clinical evaluation and advanced imaging tools that reveal changes in bone structure and tissue health. Dentists measure pocket depths around the implant, inspect for swelling, and evaluate tissue color and texture. According to our editor’s research, radiographic imaging plays a major role because it shows early bone loss patterns that cannot be seen during a visual exam. Comparing past and current images helps clinicians detect even minor changes. Accurate diagnosis guides the treatment approach and ensures that each step targets the actual severity of the condition. This thorough evaluation reduces the risk of overlooking important details. Comprehensive assessment supports predictable treatment outcomes.
Why does bacterial control form the foundation of treatment?
Bacterial control is essential because harmful bacteria drive the inflammation that leads to bone loss. Mechanical cleaning removes deposits from the implant surface and disrupts bacterial colonies that cause ongoing damage. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many professionals emphasize that thorough decontamination reduces inflammation and prepares tissues for healing. The implant surface requires careful cleaning to avoid scratching or altering its structure. Bacterial control also involves improving home hygiene routines. When patients adjust brushing and cleaning methods, their implant becomes easier to maintain. Effective bacterial reduction helps stabilize the condition and prevents further progression.
How do nonsurgical treatments support early-stage cases?
Nonsurgical treatment works well for early-stage peri-implantitis because it focuses on reducing inflammation and restoring healthier tissue conditions. Dentists remove plaque, calculus, and debris using specialized tools designed for implant surfaces. According to our editor’s research, antiseptic rinses and localized antibiotic therapies support healing by lowering bacterial presence. These methods help calm inflammation and create a cleaner environment around the implant. Nonsurgical care works best when bone loss is minimal and tissues respond positively to treatment. Regular follow-up appointments allow clinicians to monitor progress closely. Early nonsurgical intervention can prevent the need for complex procedures later.
What role does surgical intervention play in advanced cases?
Surgical intervention becomes necessary when pockets deepen or bone loss progresses beyond the reach of nonsurgical methods. Surgery allows the dentist to access deeper areas and remove infected tissue thoroughly. As a result of our editor’s reviews, many cases benefit from surgical flap procedures that expose the implant surface for better cleaning. This improved access helps clinicians reshape tissues and create a healthier structure. Surgery may also include bone grafting to rebuild lost support. These steps restore stability around the implant and encourage long-term success. Surgical intervention offers a more comprehensive approach for advanced cases.
Why is implant surface decontamination crucial during surgery?
Implant surface decontamination is vital because bacteria can cling tightly to rough implant surfaces and resist basic cleaning. Clinicians use specialized instruments, air abrasion, or laser techniques to remove bacteria fully. According to our editor’s research, the goal is to preserve the implant’s structure while eliminating contaminants that prevent healing. Clean surfaces support tissue reattachment and reduce the risk of reinfection. Each decontamination method is selected based on implant design and the severity of contamination. This careful approach enhances healing and improves treatment success. Clean surfaces form the foundation for long-term stability.
How does bone regeneration contribute to implant recovery?
Bone regeneration techniques help rebuild support around an implant affected by peri-implantitis. Surgeons place graft materials or regenerative membranes to create a protected space for new bone to form. As a result of our editor’s reviews, regenerative methods work best when bacterial control is achieved before the procedure. These techniques strengthen the bone foundation and improve implant stability. Some patients experience significant improvement when regeneration is combined with surgical cleaning. Bone growth takes time, but gradual improvement reinforces the success of treatment. Regeneration represents a promising option for restoring lost structure.
What role does laser therapy play in treating peri-implantitis?
Laser therapy supports peri-implantitis treatment by reducing bacteria and improving tissue healing without causing damage to the implant surface. Lasers help decontaminate pockets effectively and reduce inflammation. According to our editor’s research, many clinicians use lasers as an additional tool alongside mechanical cleaning. Laser energy targets harmful bacteria while supporting tissue regeneration. This method also minimizes discomfort for many patients. Combining laser therapy with other treatment steps improves overall outcomes. Laser technology continues to evolve and expand its role in care.
Why does maintenance care determine long-term success?
Maintenance care helps protect the implant after treatment by preventing recurrence of peri-implantitis. Dentists schedule follow-up cleanings and evaluations to track tissue response and address issues early. As a result of our editor’s reviews, maintenance care supports long-term health because it reinforces the steps completed during active treatment. Patients learn how to clean around implants effectively and how to avoid habits that increase risk. Regular care prevents bacteria from reestablishing themselves. Consistent monitoring builds confidence and helps maintain implant stability for years.
How do lifestyle factors influence treatment outcomes?
Lifestyle choices can affect treatment results because smoking, poor hygiene, and uncontrolled health conditions impact healing. Smoking reduces blood flow and compromises tissue recovery. According to our editor’s research, specialists often emphasize the importance of quitting smoking before undergoing treatment. Healthy routines such as balanced nutrition and frequent brushing support healing. Managing conditions like diabetes helps maintain stable inflammation levels. Lifestyle awareness empowers patients to take an active role in their recovery. Positive habits support the long-term health of dental implants.
What steps help prevent peri-implantitis in the future?
Prevention begins with consistent oral hygiene and regular dental checkups that catch early signs before they progress. Dentists emphasize brushing around the implant and using tools designed for interproximal cleaning. As a result of our editor’s reviews, prevention becomes easier when patients understand which habits protect their implants most effectively. Regular professional cleanings remove deposits that home care may miss. Following recommended maintenance guidelines ensures long-term stability. Prevention keeps implants healthier and reduces the need for complex treatment later.
Why is patient education essential in managing peri-implantitis?
Patient education empowers individuals to understand their condition and participate actively in maintaining implant health. Dentists explain the factors that contribute to peri-implantitis and the steps needed to manage it. According to our editor’s research, clear communication helps patients feel less anxious and more prepared. Educated patients follow care instructions more consistently. They recognize symptoms sooner and seek help before significant damage occurs. Strong communication strengthens the partnership between patient and clinician. This collaboration supports long-term implant success.
